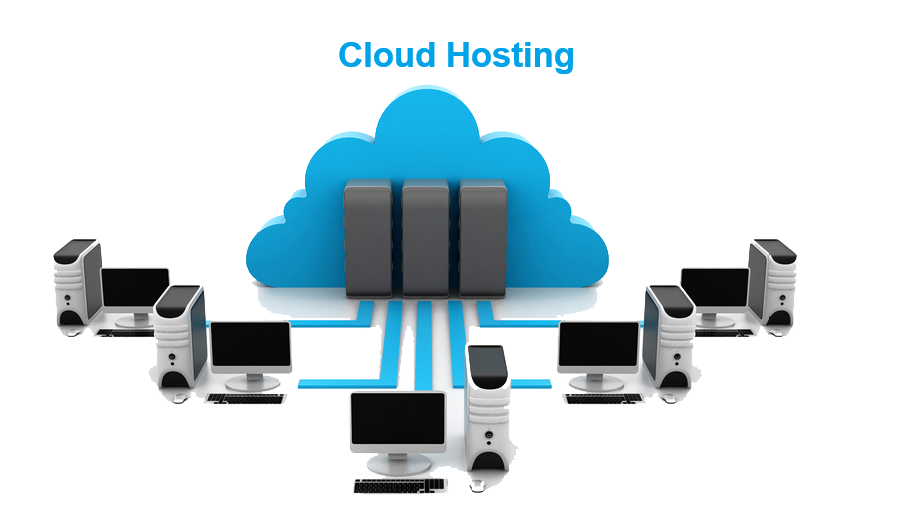
Cloud Hosting works by utilizing a network of interconnected servers to distribute resources, manage workloads, and ensure high availability for websites or applications. Unlike traditional hosting, which relies on a single server, cloud hosting spreads resources across multiple physical and virtual servers in a “cloud,” allowing for enhanced flexibility, scalability, and reliability.
Key Components of Cloud Hosting:
- Network of Servers: Cloud hosting relies on multiple servers (often spread across different data centers) that work together to store data, process requests, and deliver content to users. These servers act as a unified resource pool, providing high availability and redundancy.
- Virtualization Technology: Virtualization is used to create virtual servers that are isolated from each other but share the same underlying hardware. These virtual servers (or virtual machines, VMs) allow users to allocate resources dynamically and scale based on demand.
- Load Balancing: Cloud hosting includes load balancing mechanisms to distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers, ensuring that no single server is overwhelmed and improving response times and performance for end users.
- Resource Pooling: CPU, memory, storage, and bandwidth are pooled across the cloud servers, allowing users to access more resources than they would have on a single server. Resources can be dynamically assigned to users as demand increases, preventing bottlenecks.
- Data Redundancy and Replication: Data is often replicated across multiple servers, ensuring data protection and redundancy. This setup helps prevent data loss and provides continuous data availability, even if one server experiences failure.
How Cloud Hosting Works Step-by-Step
- User Request: When a user visits a website hosted on the cloud, the request is sent to a virtual server on the cloud infrastructure rather than a single physical server.
- Load Balancing: The load balancer directs the request to the server with the optimal performance level. If one server is under heavy load, it sends the request to a different server within the cloud to ensure fast response times.
- Resource Allocation: The cloud hosting platform automatically allocates the necessary resources (CPU, RAM, storage, etc.) to process the request. This flexibility allows the site to handle fluctuating traffic smoothly, as resources can be scaled up or down instantly.
- Data Processing and Delivery: Once resources are allocated, the server processes the request, retrieves the necessary data (like web pages or application content), and sends it back to the user’s browser. If a server goes down or experiences a hardware failure, other servers take over the workload, ensuring uninterrupted service.
- Dynamic Scaling: As traffic fluctuates, cloud hosting can scale resources up during high-demand periods (e.g., a sale on an e-commerce site) and reduce resources during low-traffic times, optimizing cost and performance.
- Data Replication and Backup: Throughout this process, data is backed up and often replicated across several servers within the network, ensuring redundancy and protecting against data loss.
Benefits of Cloud Hosting in Practice:
- Scalability: Cloud hosting makes it easy to scale resources according to demand.
- Reliability: Multiple servers provide redundancy and high uptime.
- Cost Efficiency: Pay-as-you-go pricing allows businesses to only pay for the resources they use.
- Performance: Load balancing and resource pooling reduce latency and enhance site speed.
- Flexibility: Users can access a wide range of configurations and software options.
Cloud Hosting Use Cases:
Cloud hosting is suitable for various use cases, including e-commerce sites, applications with fluctuating traffic, content-heavy sites, and businesses requiring high availability and redundancy. Its adaptability makes it ideal for rapidly growing websites and applications that need robust performance and flexibility to handle changing user demands.
Here’s a list of 50 cloud hosting providers, covering a mix of popular, niche, and specialized providers across the globe. They vary in services, with some offering comprehensive cloud platforms (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) and others focusing on specific types of cloud hosting.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- IBM Cloud
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- Alibaba Cloud
- DigitalOcean
- Linode
- Vultr
- OVHcloud
- Rackspace Technology
- Salesforce Cloud
- SAP Cloud Platform
- Adobe Cloud
- Tencent Cloud
- Heroku
- Kamatera
- CloudSigma
- UpCloud
- Hetzner Cloud
- Liquid Web
- DreamHost
- InMotion Hosting
- GreenGeeks
- A2 Hosting
- HostGator Cloud
- SiteGround Cloud Hosting
- Hostinger Cloud
- Kinsta
- Cloudways
- Scala Hosting
- IONOS by 1&1
- FastComet
- Bluehost Cloud
- HostPapa Cloud
- Alibaba Cloud
- Lightsail by AWS
- Atlantic.net
- AccuWeb Hosting
- Nexcess
- VPS.net
- Aruba Cloud
- Clouvider
- Fujitsu Cloud
- CenturyLink Cloud (Lumen)
- Leaseweb
- PhoenixNAP
- IBM Cloud Foundry
- T-Systems
- Scaleway
These providers offer a wide range of cloud hosting solutions, from managed cloud hosting to enterprise-level infrastructure, suitable for various needs, from startups and small businesses to large enterprises and government organizations.