What is Cybersecurity ?
Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting internet-connected systems, like servers, software, mobile devices, networks, and data, that contain sensitive information from cyberattacks.
Cybersecurity, also known as IT security, involves measures designed to protect organizations from both internal and external threats. In simple terms, cybersecurity helps organizations safeguard their computer systems and data centers from unauthorized access.
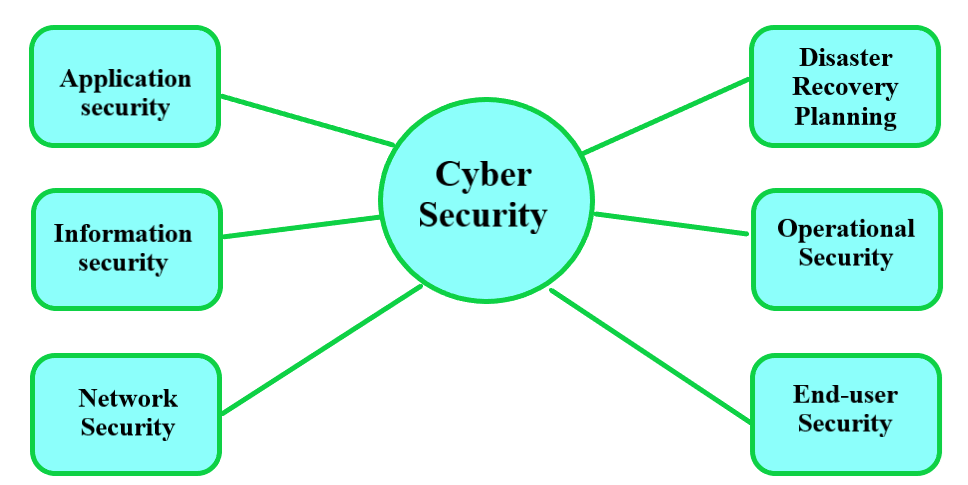
Key domains that cybersecurity measures should address include:
1. Network Security
Security strategies aimed at protecting network-connected resources and preventing unauthorized access to systems and data.
2. Cloud Security
Protecting data in the cloud—whether at rest, in transit, or in use—by encrypting it and ensuring compliance with regulations, business needs, and user privacy expectations.
3. Application Security
Integrating security protocols during the design and development of software applications, focusing on secure user authentication and data handling.
4. Critical Infrastructure Security
A U.S. security initiative focused on protecting interconnected systems, assets, and networks essential for public safety, national defense, and economic stability.
5. End-User Security
Implementing layered, end-to-end protection tools—such as firewalls, email filtering, web security, and endpoint protection—to safeguard users and their devices.
6. Disaster Recovery
The process of ensuring that an organization’s systems and infrastructure can be quickly restored after events like cyberattacks, power outages, or natural disasters, minimizing downtime and data loss.
7. Information Security
Applying policies like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and exposure.
8. Storage Security
Securing data storage systems and their contents through encryption and the isolation of backup copies, enhancing resilience against cyberattacks.
9. Mobile Security
Protecting confidential data on mobile and portable devices—such as smartphones, laptops, wearables, and voice assistants—through specialized cybersecurity techniques.
How Does Cybersecurity Work ?
Cybersecurity works by combining technology, processes, and people to protect systems, networks, and data from cyber threats like hacking, malware, ransomware, phishing, and more.
1. Threat Prevention
The first goal of cybersecurity is to stop attacks before they happen.
- Firewalls: Block unauthorized network traffic
- Antivirus/Anti-malware: Detect and remove malicious software
- Access Control: Only authorized users can access systems (via usernames, passwords, biometrics, etc.)
- Encryption: Data is scrambled to protect it from being read if stolen
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Identity and Access Management (IAM). It defines the roles of each user and sets access privileges accordingly. IAM streamlines the control and connects users with the required resources. Multi-factor authentication, single-sign-on, and lifecycle management are a few IAM methodologies that are used by businesses to minimize cyber threats.
- Zero Trust Security: It is the cybersecurity measure that requires every user whether inside or outside the enterprise to authorize, authenticate, and validate security configurations for accessing data or applications. Zero Trust Security system follows the never trust, always verify principle. Preventing lateral movement, adding strong authentication methods, and leveraging network segmentations are some of the ways used in Zero Trust Security to protect system environments.
2. Threat Detection
If something suspicious happens, systems try to detect it quickly.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Monitors logs and events.It is a cybersecurity method that collects and analyzes security events data to detect any sort of suspicious activity and triggers a preventive response. SIEM methods now use advanced technologies for better detection like artificial intelligence and behavioral analysis.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Watches computers and devices for signs of attack
- Data Security Platform: It is a security solution that combines traditional security tools to protect data across multiple environments, offer real-time visibility, and continuous monitoring of data vulnerabilities to alert to avoid corruption, data theft, or unauthorized access.
3. Incident Response
When a breach or threat is detected, cybersecurity teams take action to contain and fix it.
- Isolate affected systems
- Analyze the attack (forensics)
- Patch vulnerabilities
- Restore backups if needed
4. Recovery and Improvement
Post-incident, cybersecurity involves learning and adapting:
- Update systems and security policies
- Train employees
- Conduct audits and testing (like penetration tests)
Cybersecurity Lifecycle
- Identify – What assets need protection?
- Protect – Implement security controls
- Detect – Monitor systems for threats
- Respond – Take action on incidents
- Recover – Restore systems and operations
Human Element
Technology isn’t enough. People play a crucial role:
- Employees must avoid phishing attacks
- Security teams must monitor and respond to alerts
- Developers must write secure code
Real-World Example
Imagine your email has two-factor authentication (2FA):
- Even if someone guesses your password, they can’t get in without your phone.
That’s cybersecurity in action — layering defenses to reduce risk.
What is Cybersecurity ? Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting internet-connected systems, like servers, software, mobile devices, network
[See the full post at: How Does Cybersecurity Work ?]
How Does Cybersecurity Work ?
ICS Tutorial
Related posts:
Related posts: